What Is Gallbladder Cancer?
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ situated just below the liver. Its main role is to store bile—a digestive fluid that helps break down fats during digestion.
Gallbladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells begin to grow uncontrollably in the gallbladder. One of the challenges with this cancer is that it often doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages. Because of its deep location in the body, early detection can be difficult.
If found early, gallbladder cancer may be treated successfully. However, when diagnosed at a later stage, it becomes more challenging to manage, as the cancer may have spread to nearby organs.
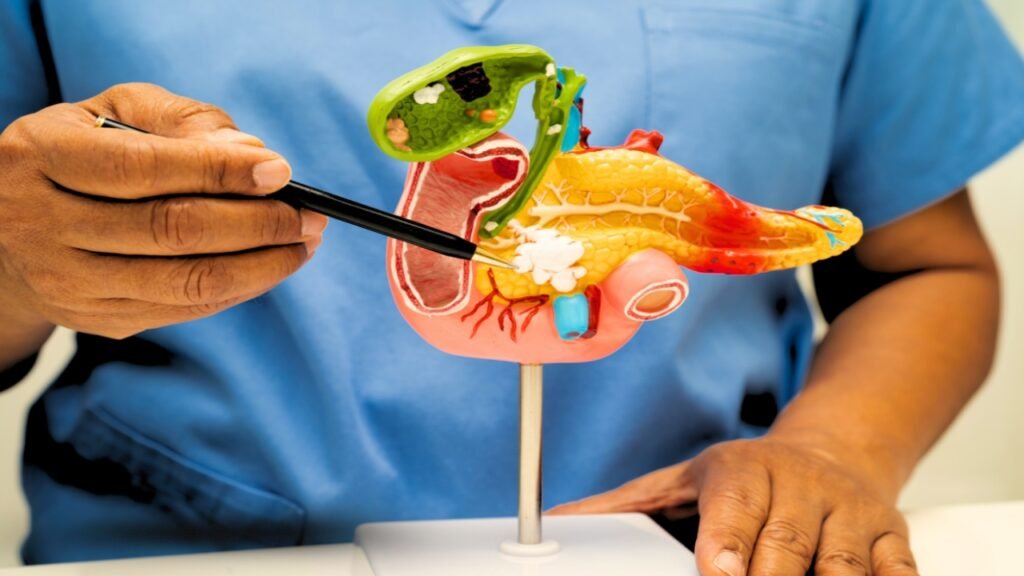
What Causes Gallbladder Cancer?
To offer effective Ayurvedic care for gallbladder cancer, it’s important to understand what might trigger the condition.
Gallbladder cancer begins when healthy cells in the gallbladder undergo genetic mutations. These mutations cause the cells to grow abnormally, forming a mass or tumor. Over time, these cancerous cells can spread to other parts of the body.
Several factors may increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer:
Gender and Age: Women are more likely than men to develop gallbladder cancer, and the risk increases with age.
Gallstones: A history of gallstones is one of the most common risk factors. Gallstones can cause long-term irritation and inflammation, which may lead to cancer over time.
Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation: Ongoing inflammation or infections in the gallbladder raise the likelihood of abnormal cell changes.
Gallbladder Polyps: These growths in the gallbladder lining may turn cancerous in some cases.
Bile Duct Disorders: Conditions such as primary sclerosing cholangitis, which inflame and scar the bile ducts, can contribute to the development of gallbladder cancer by affecting bile drainage from the liver and gallbladder.

What Are the Types of Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder cancer is classified based on the type of cells where the cancer begins. Understanding the type helps doctors decide the most effective treatment plan.
1. Adenocarcinoma
This is the most common type of gallbladder cancer. It begins in the glandular cells of the gallbladder lining, which produce mucus.
There are three subtypes:
Non-papillary adenocarcinoma: Most common and tends to spread quickly.
Papillary adenocarcinoma: Less common and less likely to spread; it starts in the connective tissues that hold the gallbladder.
Mucinous adenocarcinoma: Characterized by the presence of mucus-filled cancer cells.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
This type starts in the squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells found in the lining of the gallbladder. It is less common and often more aggressive.
3. Adenosquamous Carcinoma
This rare type contains both glandular (adenocarcinoma) and squamous cancer cells. It is considered a mixed form and may behave more aggressively.
4. Small Cell Carcinoma (Oat Cell Cancer)
A very rare type that resembles the structure of oats under a microscope. It grows rapidly and is typically difficult to treat.
5. Sarcoma
Sarcomas originate in the connective tissues such as blood vessels, muscles, or nerves within the gallbladder wall. These are also rare and can be challenging to detect in early stages.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder cancer often goes unnoticed in the early stages, as it usually doesn’t show clear symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, certain signs begin to appear, which can indicate an underlying problem in the gallbladder.
Here are some of the common symptoms associated with gallbladder cancer:

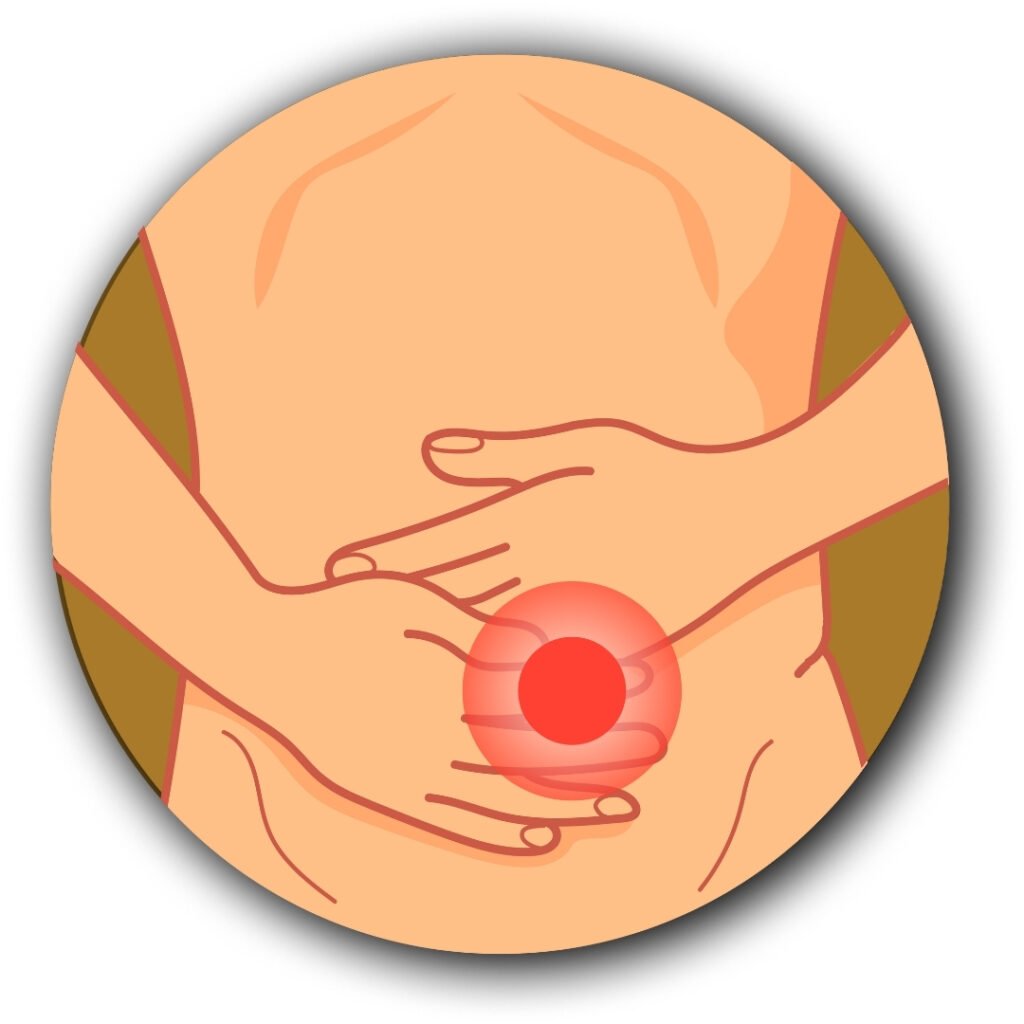
Pain in the Upper Right Abdomen:
A persistent ache or discomfort below the ribs on the right side is often one of the first signs.

Bloating or a Full Feeling:
Many patients experience a sense of heaviness or bloating in the abdomen.

Jaundice:
Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, a sign that the bile ducts may be blocked.

Sudden, Unexplained Weight Loss:
Losing weight without changes in diet or exercise can be a red flag.

Nausea and Vomiting
Often accompanied by a loss of appetite.

Fever:
A low-grade, persistent fever may be present in some cases.
Abdominal Lumps or Masses
A lump may be felt in the abdomen due to enlarged gallbladder or liver.
What Are the Complications of Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder cancer can lead to several complications, especially when it’s not diagnosed or treated early. Because the gallbladder is located close to many vital organs, the disease can spread quickly, making management more challenging.
A New Approach to Cancer Healing
at Raghavan Cancer Care
At Raghavan Cancer Care, treatment goes beyond just managing cancer — it’s a complete journey toward physical, emotional, and spiritual wellness.

Metabolic Healing
Dr. Raghavan follows a powerful method inspired by Dr. Thomas Seyfried, focusing on the unique way cancer cells use energy. By supporting the body through special approaches like a ketogenic diet, this method offers a fresh direction in cancer care rooted in metabolic understanding.

Mind-Body Balance
Taking inspiration from Dr. Joseph Mercola, our care also emphasizes the deep link between the mind, body, and spirit. At Raghavan Cancer Care, we believe that emotional and spiritual support is just as important as physical treatment in the healing process.

Food as Medicine
Dr. Wallach’s nutritional guidance has shaped our strong focus on diet. We promote clean, nutrient-rich meals and personalized nutrition plans to help strengthen the body and support recovery naturally.
